Memory, Sound and Display Technologies
This part of the article will be about the different technologies that exist for memory, sound and displays.
Memory
Memory is the most important component in a computer, without any memory in a computer, no processes would be able to run effectively, as even the CPU has its own memory (cache). Computers will also have separate memory modules (RAM), which store information that is being processed by the CPU. This saves the CPU from reading from the hard drive constantly, which would result in the computer operating very slowly. As it is random access memory (RAM), it is taken when it is required by the system.

Here is a diagram to show the effectiveness and price of different forms of memory.
There are different types of memory, used for handling different processes inside a computer.
RAM is the most heard-of type of memory in a computer, as I aforementioned, it is accessed randomly, as it handles processes out-of-order. RAM isn't only found in consoles and computers, it is also found in many electrical devices, such as printers, to store things such as upcoming print jobs. The information stored in ram is flushed out when the power to it is lost, making it temporary.
There are a few main types of RAM:
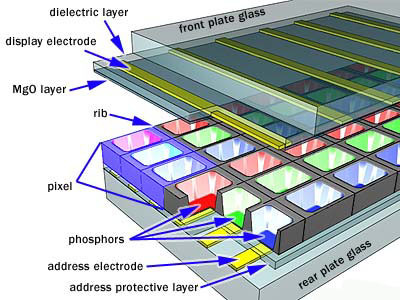 Most displays these days are LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). LCDs work by turning on and off pixels, by using liquid crystals. Light is shone through different liquid crystal filters, which control the light and colour levels, which end up in the form as different coloured pixels. As a pixel is made up of 3 sub-pixels, of blue, green and red, when combined, they can display 16.7 million colours (256 shades of each colour).
Most displays these days are LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). LCDs work by turning on and off pixels, by using liquid crystals. Light is shone through different liquid crystal filters, which control the light and colour levels, which end up in the form as different coloured pixels. As a pixel is made up of 3 sub-pixels, of blue, green and red, when combined, they can display 16.7 million colours (256 shades of each colour).
The amount of pixels lengths-ways multiplied by the amount up and down is the resolution (e.g 1080x1920 = 2,073,600 pixels)
All LCD displays will have a resolution, for example the New 3DS has a 800x240 resolution (top screen), and the iPad Air 2 has the resolution of 2048x1536. Obviously, the higher the resolution, the clearer and more expensive the display.
4K is a 'new' technology, that has only been made available for a few months now, which is the resolution 3840x2160. This is obviously a very crisp resolution, but for a console or PC to run this resolution natively in game, it would need very beefy hardware. For PCs, if the player wants to achieve high graphical detail in their games at 4K, they would most definitely need an SLI or CrossFireX configuration (multiple GPUs).
With the evolution of technology, today's games have rich, 3D, highly realistic and cinematic sounds, capable of being multi-layered. You can play pretty much every modern game nowadays in full surround sound, if you own even the cheapest 5.1 or 7.1 speaker setup. Capturing and recording sounds is also made easy and high quality, with sound cards. Sound cards have four main, notable components:
The way that the ATC (Analog-to-Digital) and the DTA (Digital-to-Analog) converters work, is that a microphone input would take the analog sound of whatever you are recording, and convert it to a digital file, and if you are playing a digital sound file from a computer, it will be converted to analog sound. An analog sound is recorded by taking measurements of the analog wave, and measuring them. These measurements are measured as kilohertz (KHz), and are known as the sampling rate, so the better the sound card, the more samples can be taken, the higher quality the sound is. As an alternative to sound cards, consoles can have an MCP (Media Communications Processor), which works the same as an intergrated sound chip.
It is easy to confuse 3D sound and surround sound. 3D sound is what is recorded into a game, which is what allows the player to pinpoint what is going on in the game, and it moves with the player accordingly. Surround sound refers to the speaker set up, which is common in home theatre systems.
So, that is my section on Memory, Sound and Display technologies current of today, plase stay tuned for more!
Matt :3

Here is a diagram to show the effectiveness and price of different forms of memory.
Types of Memory
There are different types of memory, used for handling different processes inside a computer.
RAM is the most heard-of type of memory in a computer, as I aforementioned, it is accessed randomly, as it handles processes out-of-order. RAM isn't only found in consoles and computers, it is also found in many electrical devices, such as printers, to store things such as upcoming print jobs. The information stored in ram is flushed out when the power to it is lost, making it temporary.
There are a few main types of RAM:
- DRAM
DRAM is the most common type of RAM, as it cheaper to produce. DRAM stands for dynamic RAM. Dynamic RAM is dynamic, because it gets refreshed thousands of times per second. It refreshes so much because the chips are made of lots of transistors and capacitors, so the capacitors leak information, thus needing to be refilled by the CPU.
- SRAM
SRAM is static RAM, which is different to dynamic RAM, as it does not need to be refreshed, therefore making it more expensive to produce. As it does not need to be refreshed, it makes it much faster RAM too. SRAM is only used in parts of a computer where it needs to be fast, as most computers and consoles will use a combination of both SRAM and DRAM. As SRAM does not need to be refilled, it stops the need for the CPU to fill it with information again.
- RDRAM
RDRAM is an abbreviation of Rambus Dynamic RAM. RDRAM is one of the fastest types of RAM available to systems. It works similarly to that of DRAM, but can achieve quicker speeds, due to a higher end data bus. RDRAM requires a specialist motherboard, to utilize its full potential. A lot of consoles utilise RDRAM, the first to do this being the Nintendo 64.
- SDRAM
Display
 Most displays these days are LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). LCDs work by turning on and off pixels, by using liquid crystals. Light is shone through different liquid crystal filters, which control the light and colour levels, which end up in the form as different coloured pixels. As a pixel is made up of 3 sub-pixels, of blue, green and red, when combined, they can display 16.7 million colours (256 shades of each colour).
Most displays these days are LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). LCDs work by turning on and off pixels, by using liquid crystals. Light is shone through different liquid crystal filters, which control the light and colour levels, which end up in the form as different coloured pixels. As a pixel is made up of 3 sub-pixels, of blue, green and red, when combined, they can display 16.7 million colours (256 shades of each colour).The amount of pixels lengths-ways multiplied by the amount up and down is the resolution (e.g 1080x1920 = 2,073,600 pixels)
All LCD displays will have a resolution, for example the New 3DS has a 800x240 resolution (top screen), and the iPad Air 2 has the resolution of 2048x1536. Obviously, the higher the resolution, the clearer and more expensive the display.
4K is a 'new' technology, that has only been made available for a few months now, which is the resolution 3840x2160. This is obviously a very crisp resolution, but for a console or PC to run this resolution natively in game, it would need very beefy hardware. For PCs, if the player wants to achieve high graphical detail in their games at 4K, they would most definitely need an SLI or CrossFireX configuration (multiple GPUs).
Sound
Before rich and realistic sound for computers and consoles, they could only beep. These beeps could be put together in different pitches to make a very basic tune. Although irritating, there was no alternative in the time. Computers could not change the volume of the beeps though, or make any other sounds.
These beeps started out as a warning symbol (much like the beeps you hear on a PC boot), but did end up being manipulated into basic, non-realistic and quite frankly irritating tunes.
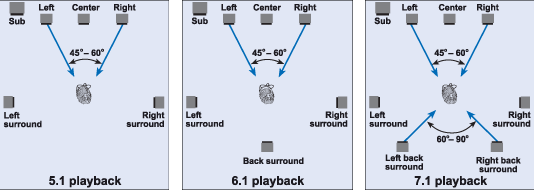
With the evolution of technology, today's games have rich, 3D, highly realistic and cinematic sounds, capable of being multi-layered. You can play pretty much every modern game nowadays in full surround sound, if you own even the cheapest 5.1 or 7.1 speaker setup. Capturing and recording sounds is also made easy and high quality, with sound cards. Sound cards have four main, notable components:
- Analog-to-digital converter
- Digital-to-analog converter
- An ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) or PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) interface to connect the sound card to the motherboard.
- Input and output connections for microphones and speakers.
Most motherboards these days actually have high quality on-board sound chips, capable of surround sound, more often than not even full 7.1 surround.
PCI Interfaces are universal, meaning they are also used for other expansion cards, such as a graphics card, or a USB expansion card.
PCI Interfaces are universal, meaning they are also used for other expansion cards, such as a graphics card, or a USB expansion card.
The way that the ATC (Analog-to-Digital) and the DTA (Digital-to-Analog) converters work, is that a microphone input would take the analog sound of whatever you are recording, and convert it to a digital file, and if you are playing a digital sound file from a computer, it will be converted to analog sound. An analog sound is recorded by taking measurements of the analog wave, and measuring them. These measurements are measured as kilohertz (KHz), and are known as the sampling rate, so the better the sound card, the more samples can be taken, the higher quality the sound is. As an alternative to sound cards, consoles can have an MCP (Media Communications Processor), which works the same as an intergrated sound chip.
It is easy to confuse 3D sound and surround sound. 3D sound is what is recorded into a game, which is what allows the player to pinpoint what is going on in the game, and it moves with the player accordingly. Surround sound refers to the speaker set up, which is common in home theatre systems.
So, that is my section on Memory, Sound and Display technologies current of today, plase stay tuned for more!
Matt :3

0 comments:
Post a Comment